IT Department: Understanding Specialist Teams and Tools

The IT department plays a vital role in managing infrastructure, ensuring efficiency, security, and smooth communication. This blog digs into the various roles, teams, and processes that define an IT department's operations, highlighting the importance of Service Level Agreements (SLAs), ITIL, agile methodologies, and specialized tools. From network administration to IT audit, we'll explore the supportive functions that keep IT running smoothly and contribute to the overall success of the business.
What is an IT Department?

An IT (Information Technology) department is a team within an organization responsible for managing and maintaining its computer systems, servers, networks, and other technology infrastructure. They ensure a smooth operation, troubleshoot issues and help implement new technologies to improve efficiency, security, and communication.
Read: An SLA with the IT department outlines the agreed-upon standards for service quality, response times, and resolution targets for issues such as hardware and software maintenance, technical support, and network uptime. Click here to read a complete guide on service level agreement definition and more
Common Types of IT Teams
There are several different types of IT teams, each with its specific focus and responsibilities. Here's a breakdown of some of the most common ones:
- Operations Team (also known as Runbook Team or Infrastructure Team)
- Project Team (also known as Delivery Team or Implementation Team)
- Process Team (also known as IT Governance Team or Compliance Team)
- Support Team (also known as Help Desk Team or Technical Support Team)

The Operations Team is responsible for the day-to-day management and maintenance of an organization's IT infrastructure. Their primary focus is on ensuring that systems are running smoothly, data is secure, and services are available to end-users. They handle tasks such as network management, server administration, database maintenance, and incident resolution. Operations teams often work behind the scenes to prevent or minimize downtime and support business continuity.

A project team is assembled to work on specific, time-bound IT initiatives or projects. These teams are usually composed of members with diverse skill sets, such as developers, business analysts, and quality assurance specialists, who collaborate to design, develop, and implement new systems, applications, or technologies. Project teams follow a defined project management methodology to ensure deliverables are met within scope, time, and budget constraints.

The Process Team focuses on improving and optimizing the various IT processes within an organization. They analyze current workflows, identify inefficiencies, and develop strategies to streamline and standardize processes. This includes areas like change management, incident resolution, service level agreements (SLAs), and ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) best practices. Their goal is to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and increase overall service quality.

The Support Team is responsible for assisting end-users with technical issues and providing timely resolutions. They handle IT help desk functions, troubleshooting hardware and software problems, and assisting with software installations or configurations. Support teams often work in a tiered structure, with Tier 1 handling basic inquiries and escalating more complex issues to Tiers 2 or 3. They strive to ensure user satisfaction and minimize disruptions to business operations.
IT Department Roles and Responsibilities
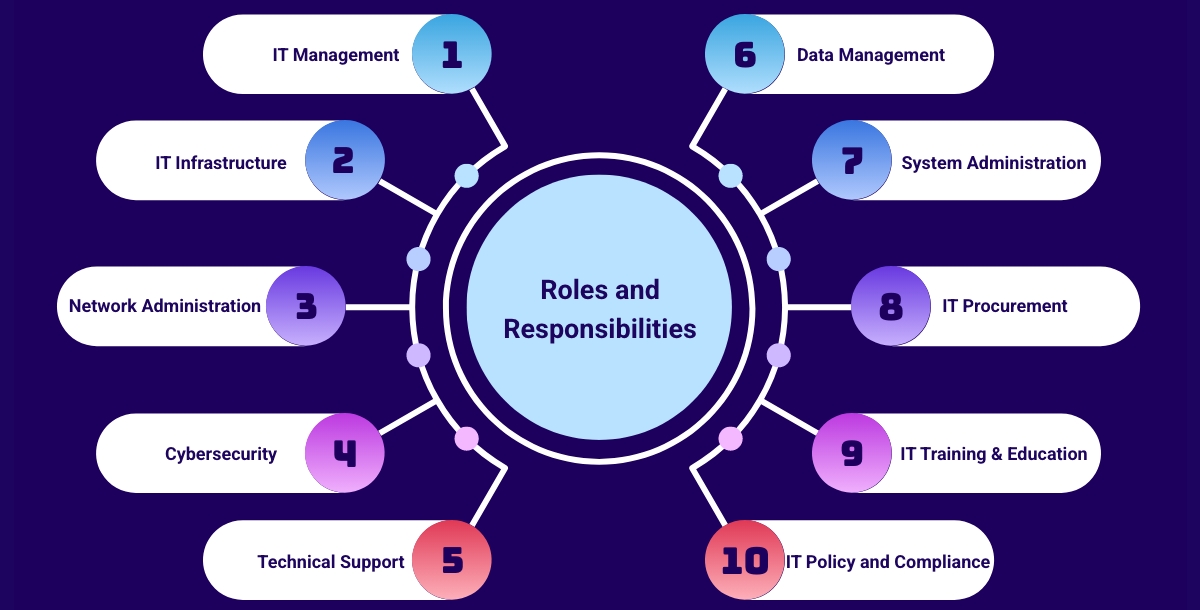
The IT department plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of an organization in terms of managing its information technology infrastructure, systems, and services. The IT department's responsibilities include:
- IT Management: Overseeing the overall IT strategy, ensuring smooth operations, and providing leadership to the IT team.
- IT Infrastructure: Designing, implementing, and managing the organization's IT infrastructure, including hardware, software, networks, and other technology resources.
- Network Administration: Ensuring the stability and security of the organization's networks, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and internet connectivity.
- Cybersecurity: Implementing and maintaining security measures to protect the organization's data, systems, and networks from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
- Technical Support: Providing technical assistance to employees, troubleshooting and resolving hardware, software, and network issues.
- Data Management: Ensuring the availability, integrity, and security of the organization's data, including data storage, backup, and recovery.
- System Administration: Managing and maintaining the organization's servers, operating systems, and applications, ensuring optimal performance and uptime.
- IT Procurement: Evaluating, purchasing, and managing IT assets, such as hardware, software, and service contracts.
- IT Training and Education: Providing training and guidance to employees on IT systems, software, and best practices.
- IT Policy and Compliance: Developing and enforcing IT policies, procedures, and standards. Ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards.
IT Organizational Structures
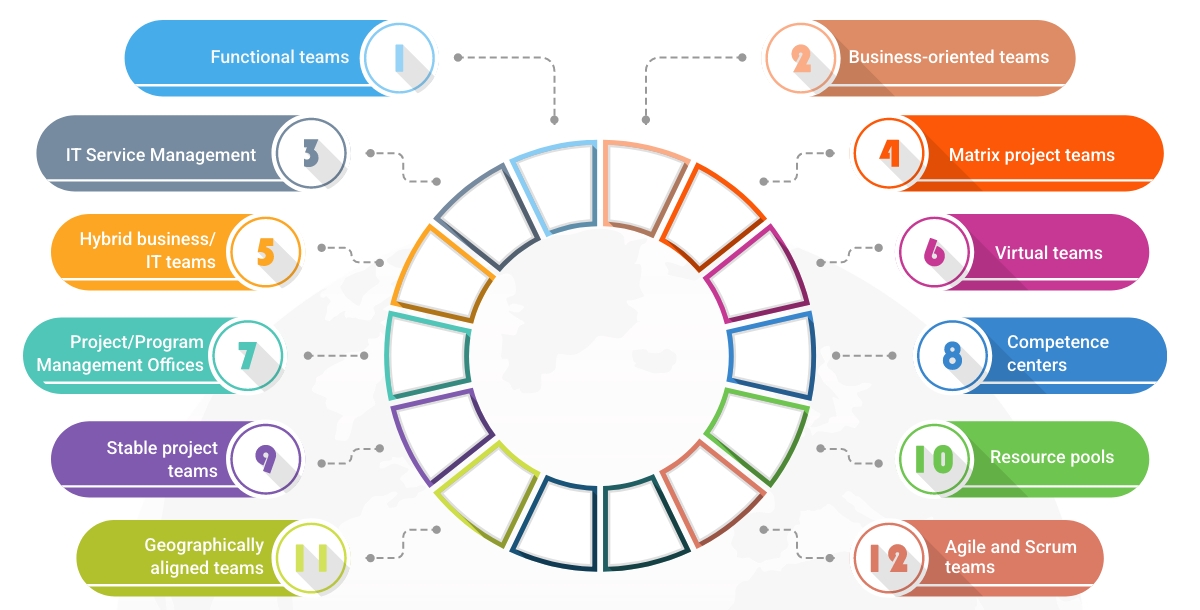
IT organizational structures can vary significantly based on the size, industry, and specific needs of a company. Here are some common IT organizational structures:
- Functional teams: These teams specialize in specific technologies or domains, such as network engineering, cybersecurity, or software development. They focus on maintaining, enhancing, and implementing technology solutions to support the organization's needs.
- Business-oriented teams: These teams are aligned with specific business units or functions, such as sales, marketing, or finance, and provide tailored IT solutions and support to meet those units' unique requirements. They often have a deep understanding of the business domain they serve.
- IT Service Management (ITSM) functional teams: ITSM teams are responsible for managing IT services throughout their lifecycle, from service strategy to service improvement. They include roles like service desk, incident management, problem management, and change management.
- Matrix project teams: As mentioned earlier, matrix teams have members reporting to both a functional manager (for their expertise) and a project manager (for project-specific tasks). This structure allows for efficient resource utilization and knowledge sharing across projects.
- Hybrid business/IT teams: These teams consist of both business and IT professionals, working together to bridge the gap between technology solutions and business objectives. They collaborate to develop and implement IT projects that directly contribute to the organization's strategic goals.
- Virtual teams: Virtual teams work remotely and across different locations, often leveraging digital tools for communication and collaboration. This structure is common in global organizations or when specialized skills are needed from various regions.
- Project/Program Management Offices (PMOs): PMOs are responsible for overseeing and standardizing project management processes, ensuring projects are delivered on time, within budget, and meet quality standards. They can also provide governance, risk management, and resource allocation.
- Competence centers: These are specialized teams that focus on developing and maintaining expertise in a particular area, such as data analytics, cloud computing, or user experience design. They serve as a knowledge hub for the organization and provide guidance and training.
- Stable project teams: These teams stay together for an extended period, working on multiple related projects or a long-term initiative. This structure fosters continuity, team cohesion, and improved performance.
- Resource pools: A pool of IT professionals with diverse skills who can be assigned to various projects as needed. This structure promotes flexibility and resource optimization, but team members may need to adapt to different project contexts quickly.
- Geographically aligned teams: Teams organized based on regional or location-based needs, allowing for a better understanding of local market conditions, language, and cultural nuances.
- Agile and Scrum teams: Following agile methodologies like Scrum, these teams work in short iterations (sprints) to deliver value quickly and adapt to changing requirements. They emphasize collaboration, self-organization, and continuous improvement.
IT Department Jobs

The IT department typically consists of various roles, each with its own set of responsibilities. Here are some common job titles found in an IT department:
- Project Manager: Leads a team of people from different areas to finish IT projects on time, and within budget, and connects them to the company's big plans. They manage resources and solve problems.
- Business and IT Analysts: Work together with different teams to understand what they need, then find and set up IT tools to make work easier, faster, and cost-effective.
- Business Process Designer: Designs and improves the way work is done and the IT systems, so things run smoothly and waste is reduced.
- IT Strategist: Plans the IT plan, choosing tech that fits the company's long-term goals. They also look for new tech to consider.
- Change Management Specialist: Manages changes related to IT, making sure the changes go well and don't upset the employees too much.
- Service Design and Development: Makes and improves IT services, thinking about how users will use them, how good they should be, and setting service expectations.
- Data Governance and Privacy Officer: Checks that the company follows rules to protect data, creates policies for handling data, and keeps information safe.
- Solution Architects: Designs complete IT systems by joining hardware, software, and networks. They make sure everything works well together and fits the company's needs.
- Information Security and Risk Manager: Protects the company's data and systems from online threats. They create rules, check for danger, and react to any security incidents.
- IT Service Management (ITSM) Practitioners: Focus on providing dependable and high-quality IT services, with roles that fix issues, solve problems, and continuously improve the service.
- Vendor Management Professional: Manages the relationship with outside companies that provide tech tools or services, making sure they work smoothly with the company's IT.
- Digital Transformation Lead: Promotes the use of digital tools to change how the company works, improve customer experience, and encourage new ideas within the company.
The Three Pillars of IT Processes
There are three fundamental sets of processes that most IT teams use as a starting point for their process development. These are:
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
- Agile Methods
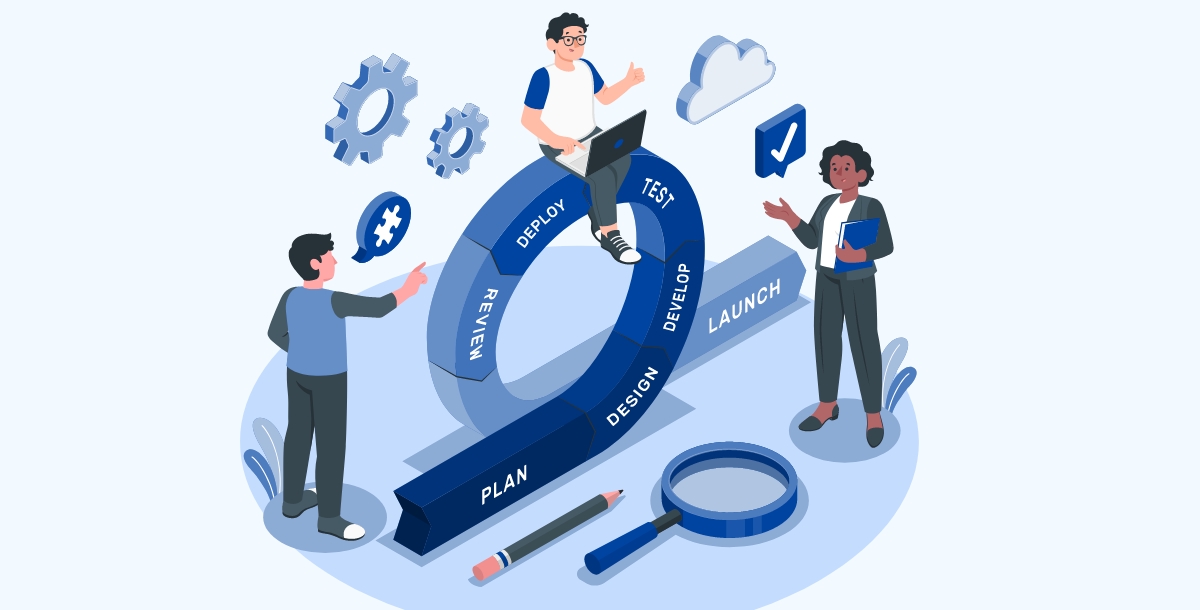

The SDLC is a framework that guides the development of new IT capabilities. It's a step-by-step process that begins with identifying a need or opportunity and ends with delivering a technological solution. The SDLC includes phases such as identification, analysis, design, development, testing, implementation, and start of operations. This framework is flexible and can be applied to various types of IT projects.

ITIL is a well-known process framework that focuses on delivering value to the organization through the operation of IT systems and services. It's a continuous improvement cycle that consists of five lifecycle phases: service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continuous service improvement. ITIL helps IT teams manage services efficiently and effectively.

Agile methodologies are changing the way IT teams work. They promote autonomy, flexibility, and collaboration. Agile teams focus on smaller pieces of work, deliver changes frequently, and adapt to changing requirements. Agile is not a set of prescribed processes, but rather a collection of principles that guide teams in defining their processes and ways of working.
Why These Processes Matter
Understanding these three pillars of IT processes is essential for every IT professional. They provide a foundation for IT teams to work efficiently, effectively, and in sync with the rest of the organization. By following these processes, IT teams can ensure that they're delivering value to the organization and meeting business needs.
Tool Functions to Support the IT Department
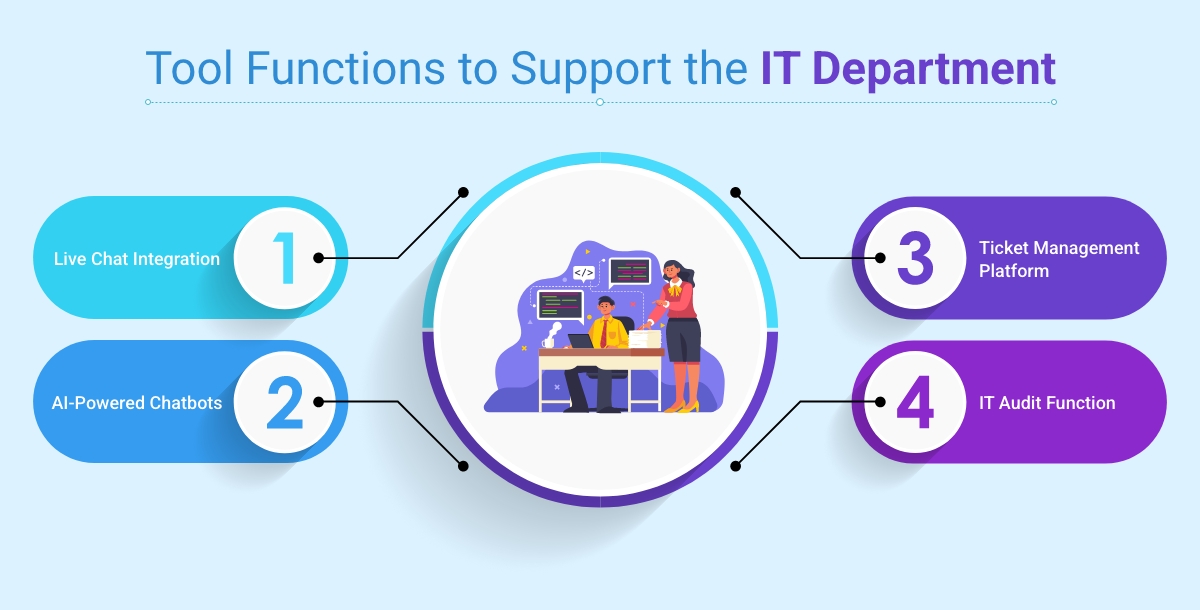
- Live Chat Integration
- Ticket Management Platform
- IT Audit Function
- AI-Powered Chatbots
A live chat tool, integrated with the IT help desk software, enables real-time communication between IT staff and employees. It allows for immediate issue resolution, reducing response times and minimizing disruption. The chat logs can be automatically fed into the ticketing system for further tracking and management.
A Ticketing system, such as IT help desk software, centralizes IT support requests. It routes tickets to the appropriate team based on expertise, assigns them for completion, and tracks their status. This tool ensures a structured and organized workflow, improving overall efficiency.
An IT audit function is responsible for evaluating the organization's IT systems, processes, and controls to ensure compliance with policies, regulations, and industry standards. This includes assessing security, privacy, and governance aspects. The audit team may use tools for data analysis, network monitoring, and vulnerability assessments.
AI chatbot are invaluable for handling routine IT inquiries. They can perform tasks like password resets, software updates, and basic troubleshooting, freeing up IT staff to focus on complex issues. These chatbots can also learn and adapt, improving their responses over time.
Conclusion
The IT department is a crucial backbone of modern organizations, managing technology infrastructure, ensuring smooth operations, and adapting to change. By understanding the various teams, processes, and tools, IT professionals can deliver efficient, secure, and communicative services that drive business success. Service level agreements, ITIL, agile methodologies, and regular audits are key to maintaining an efficient and compliant IT setup.
Related Articles
- 14 Best Order Management Software in 2023
- How to Make a Collage on iPhone: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to use pivot tables in Google Sheets? [Everything about Google Sheets Pivot Table]
- How to make eye-catching banner designs?
- Transform Your Business with a Strategic Sales Budget- Live Chat, Call Centers, and More
- Black Color: A Guide on Meaning, Symbolisms & HEX Code
- Understanding Customer Support: Definition, Importance & Strategies
- Top Zoho Books Integrations: Uplifting Accounting Operations
- How to Design a Flyer for Your Business (Step-by-Step Guide)
- Find 10 Best Meditating Apps And Learn How To Create An App
