What is a Balance Sheet And How To Create It? (With Examples)

As a business owner it is important for you to make the most of every tool that is available to run a better business. That’s why every entrepreneur should take advantage of the balance sheet. Payments are not made immediately in most of the businesses. Some companies have assets, owe funds to tax authorities, and have liabilities. All this can be calculated by using Balance Sheet accounts. So, if you run a small or a big organization, you will need to include balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements in financial reports to tax and regulatory authorities and shareholders.
(Above video is a part of a more elaborate course on Academy by Appy Pie. To access the complete course, please Click Here, or continue reading below.) A Balance Sheet is essential for a business owner looking for additional debt or equity financing. Investors prefer examining the amount of cash on the Balance Sheet.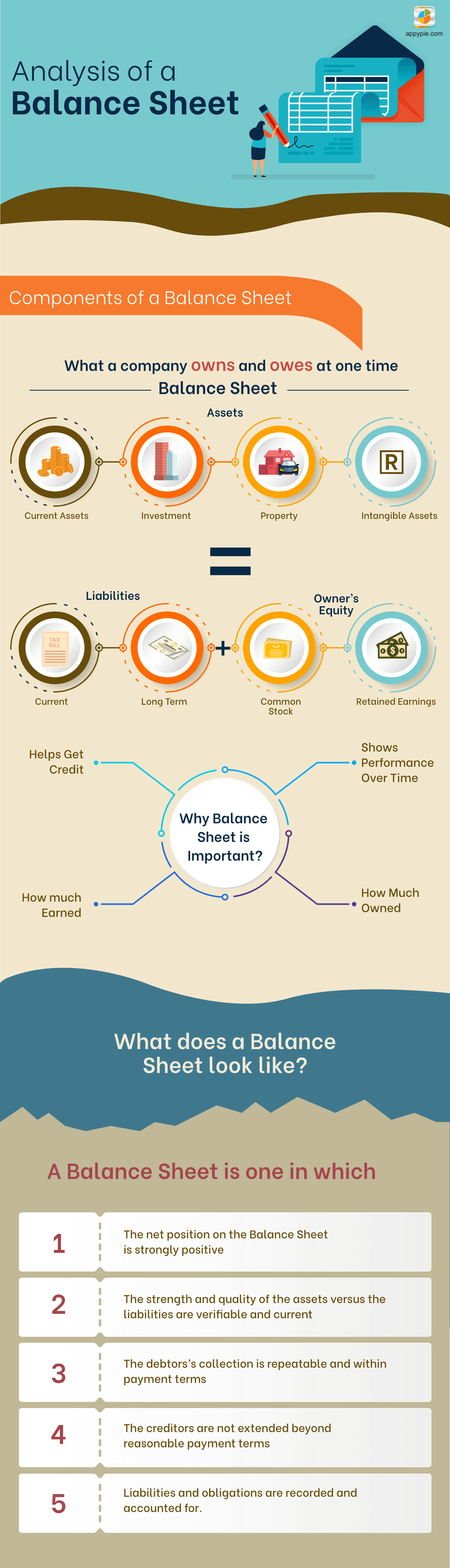 This blog will provide you with details on what is a Balance Sheet and it also includes some great Balance Sheet examples.
This blog will provide you with details on what is a Balance Sheet and it also includes some great Balance Sheet examples.What is a Balance Sheet?
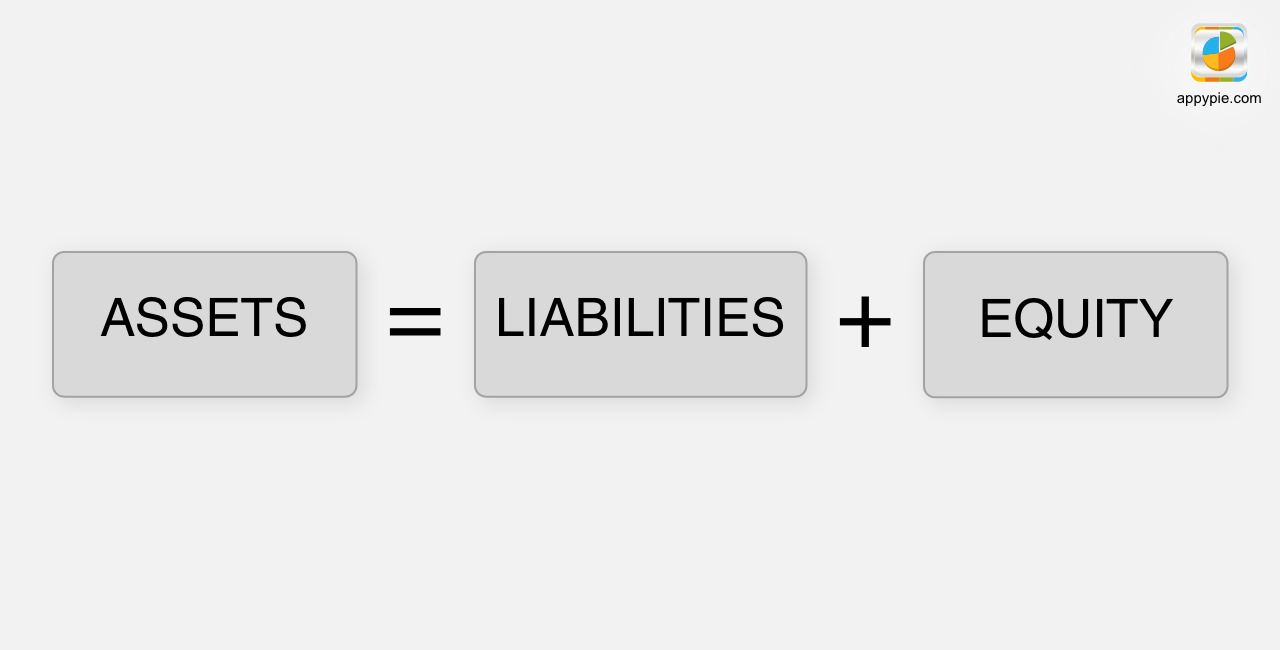
A balance sheet is a statement of the financial position of a business that lists the assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at any given time. A balance sheet illustrates your business's net worth. Balance sheet can also be termed as the statement of the financial position of an organization. The balance sheet is the most important aspect of accounting and is used to illustrate the financial health of a business. The other two important aspects are:- The income statement which shows net income for a specific period of time, such as a month, quarter, or year.
- The cash flow statement which shows the movement of cash and cash equivalents in and out of the business.
- Assets - Anything that has value and is owned by a company.
- Liabilities - Anything that provides a list of debts a company owes to others.
- Equity - This is the amount invested by the Shareholders.
Assets
Assets are typically organized into liquid assets that include cash or things that can easily be converted into cash, and non-liquid assets that cannot quickly be converted to cash, such as land, buildings, and equipment. The list of assets may also include intangible assets which are more difficult to value. These are reported on the balance sheet at the original cost minus depreciation. This includes items such as:- Franchise agreements
- Copyrights
- Patents
Liabilities
Liabilities are funds owed by any business and are categorized into current and long-term. Liabilities are obligations to parties other than owners of a business. Current liabilities are those that are due within one year and include items such as:- Accounts payable (supplier invoices)
- Wages
- Pension plan contributions
- Income tax deductions
- Medical plan payments
- Utilities
- Building and equipment rents
- Customer deposits (advance payments for goods or services to be delivered)
- Temporary loans, lines of credit or overdrafts
- Maturing debt
- Interest
- Sales tax and/or goods and service taxes charged on purchases
Equity and Earnings
Equity or shareholders' equity is the amount which remains after subtracting liabilities from the assets. If you are the sole proprietor of your business, this is referred to as the owner’s equity. If your business is a corporation, equity is referred to as stakeholder’s equity. Retained earnings are earnings retained by the corporation that are not paid to shareholders in the form of dividends.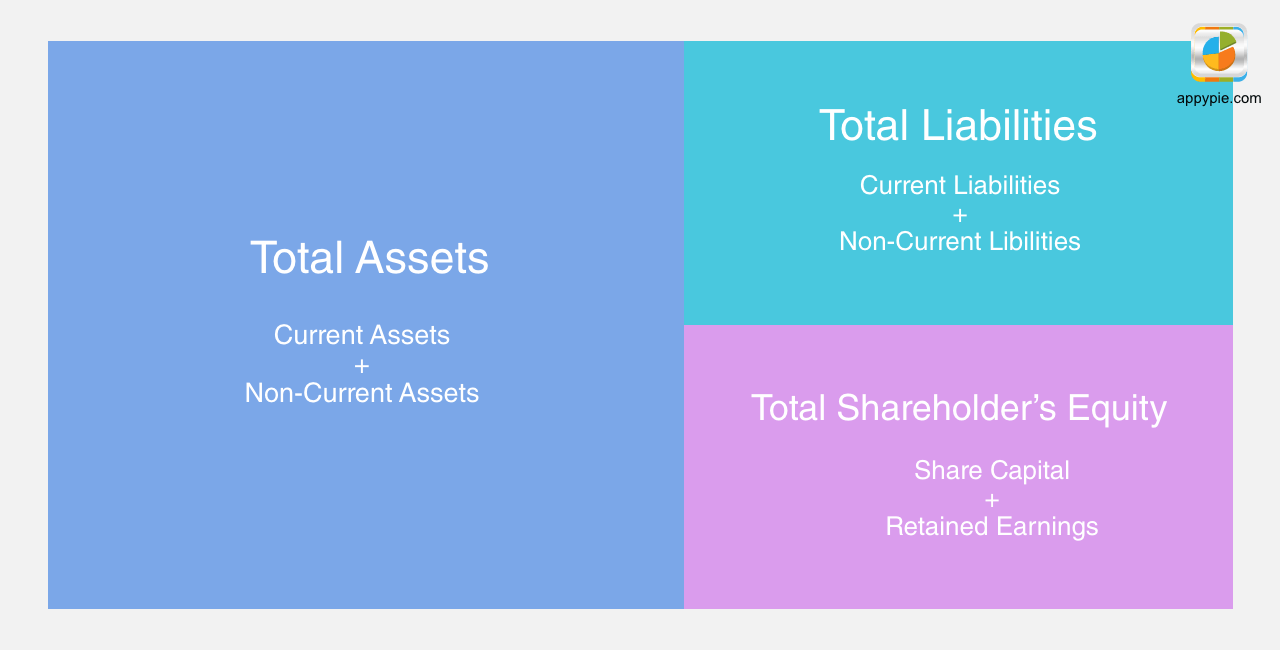
Balance Sheet Formats
There are two formats of presenting a balance sheet – account format and report format. In account format, the balance sheet is divided into the left side and the right side like a T account. The assets are listed on the left side whereas both liabilities and owners’ equity are listed on the right side of the balance sheet. If all the elements of the balance sheet are correctly listed, the total on the asset side must be equal to the total on the liabilities and owners’ equity side. In report format, the balance sheet elements are presented vertically i.e., assets are presented at the top and liabilities and owners’ equity are presented below the assets section. Using all the available information we can prepare a balance sheet. The balance sheet examples are shown below:Balance Sheet Sample 1 Balance Sheet Sample 2
Balance Sheet Sample 2
Importance of a Balance Sheet
By now it is clear that balance sheets are critical documents because they keep the business owners informed about their company’s financial standing. The Balance Sheet reveals a lot of important information about any company’s performance. Here is a list of reasons why a balance sheet is important:It is an important tool used by investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to understand the financial health of a company.
The growth of an organization can be understood by comparing the balance sheet of 2 different years.
It is an essential document that needs to be submitted to the bank for getting a loan.
Stakeholders can understand business performance of the entity.
Ability to undertake expansion projects and unforeseen expenses can be determined by reading a balance sheet.
Limitations of a Balance Sheet
Even though a Balance Sheet is important there are few limitations to it. There are 3 primary limitations to Balance Sheets, like they are recorded at historical cost, they use estimates, and they omit valuable things. Here is the list of limitations:Many items have financial value and may be important for the users but are not reported in the balance sheet because they cannot be objectively measured. Examples of such items are skill and knowledge of an IT company.
The current fair value of various assets and liabilities may be important but the balance sheet does not disclose it.
The value of some items is reported in the balance sheet on judgments and estimates. For example, depreciation is usually calculated on estimation.
Conclusion
Balance-sheet is an essential financial statement that plays an important part while taking critical financial decisions in an informed manner. It is a good idea to have an accountant do the first balance sheet for you, particularly if you are new to the business. Balance sheets are easy to manage if you use good accounting software. Accounting software designed for small businesses can keep track of all your accounting information and generate balance sheets, cash flow statements, and other reports automatically as needed. Did you know that you can manage your business accounts in a simple way? Appy Pie Connect now helps you connect your Accounting apps & software you use every day to automate your work.Related Articles
- How to Write Effective ChatGPT Prompts for the Best Results
- Exceptional Qualities of A Great Leader
- How to Make a Chatbot From Scratch?
- Christmas Background: Traditions, Evolution, and Practical Tips
- How to Chat with Your Google Sheets
- How to Change Zoom Background: A Simplified Guide
- Overview of the concept of AI Text to Video Generation
- What is a webinar and how to create a good one?
- Discord Profile Picture Size: The Ultimate Guide
- Can Feedback Enhance Semantic Grounding in Large Vision-Language Models?
Take a Related Course
- Start learning for free
(No credit card required)
