How to write an Executive Summary for your Business Plan?

An executive summary of a business plan is an overview of it. Its purpose is to summarize the key points of the document for its readers, saving them time. When you are developing a business plan, potential investors or other stakeholders will often want to see an executive summary at the beginning to get an overview of the plan. An Executive summary is often called the most important part of the business plan. If it does not capture the reader's attention, the plan will be set aside unread - a disaster if you've written your business plan as part to start your new business. As the executive summary presents the essence of the report, it should focus on the most important information without delving into minor details. Most importantly, it should be interesting enough to compel the reader to go through the complete document. This blog post has been created to explain how to write an executive summary. Even though it may vary depending upon the nature and objective of the report, and the audience it is intended towards, an executive summary should broadly touch upon:
- Unique selling proposition
- Market or target customers
- Company description and its legal form
- Pain points and your solution or funding requirement
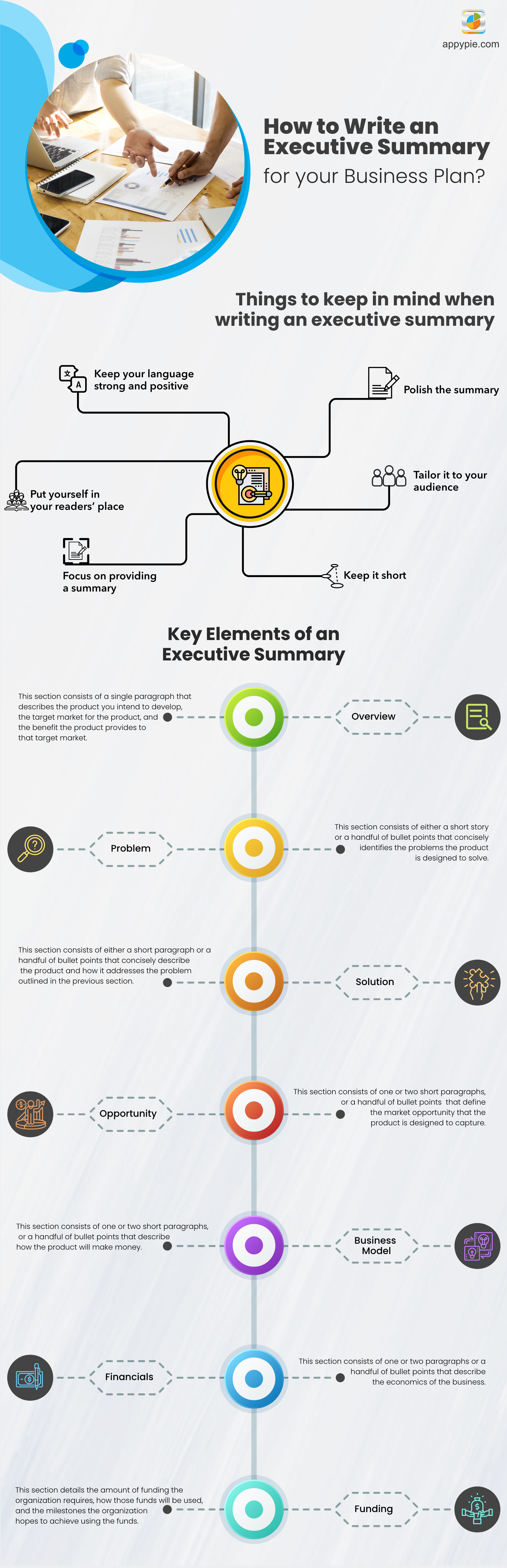
Tips on How to write an Executive Summary
Focus on providing a summary
Keep your language strong and positive
Keep it short - no more than two pages long
Polish your executive summary
Tailor it to your audience
Put yourself in your readers’ place
Key Elements of how to write an Executive Summary for a business plan
Overview
Problem
Solution
Opportunity
Business Model
Financials
Funding
#1. Overview
This section describes the product you intend to develop, the target market of the product, the competitors for the product, and how the product is different from competitive solutions in the market. An overview paragraph might look like this: <Product name> is a <type of product/category description> that delivers <statement of benefit>. Unlike <specific competitor or competitive category>, <product name> provides <statement of differentiation>.Example -
PayPal is a web-based payment service that allows buyers and sellers to transfer funds promptly while protecting against any fraud or theft. PayPal allows any merchant to accept funds and allows customers to pay without disclosing sensitive banking or personal information.#2. Problem
This section identifies problems that your product is designed to solve. Remember to use declarative sentences with very simple words to communicate each and every point.Example -
Small web-based merchants are now unable to sell their goods online due to the inability to process credit cards. Processing a credit card requires a merchant to obtain a merchant account from their bank, something that is currently expensive for small online merchants. At the same time, customers are currently hesitant to disclose their credit card number to merchants online, due to the risk of fraud. As a result, many merchants are unable to capitalize on the World Wide Web to reach and sell to new customers.#3. Solution
This section describes the product and how it addresses the issue outlined in the problem section. It is best to describe the product in terms of the benefits to the customer, and not focus on the features of the technology.Example -
PayPal provides a web-based payment service that can be used by any merchant to accept payments online. Users create a PayPal account linked to their bank account and use it to pay for goods without revealing their credit card or banking information. PayPal transfers money between customers and merchants and also protects both parties from any fraudulent transaction. Merchants get access to paying customers they are currently unable to access without a merchant account, and customers gain the ability to make risk-free online purchases.#4. Opportunity
This section describes the market prospect that the product is designed to capture. It is extremely important to cover the estimated size of the market, the estimated growth of the market, and the characteristics of the target customer.Example -
Online retail sales in 1999 reached USD X dollars, a growth of X percent over the previous year. By XXXX, XYZ estimates that online commerce will comprise USD X dollars annually or X percent of all retail sales. Currently, only X percent of the X small merchants making less than USD X annually are currently exploiting the Internet to reach customers online. A web-based payment processing system would remove this barrier, and permit an estimated USD X in additional online transactions to occur annually.#5. Business Model
This section describes how the product will make money. How does the customer purchase the product? Is the product sold to the customer directly or provided on subscription-basis? Is there some other way that business makes money? How much money does the company make on each sale?Example -
PayPal derives revenue from each transaction it processes. Customers pay nothing to transfer funds to a merchant using the service, but merchants pay between 1.9 percent and 2.9 percent, depending on the dollar value of the transaction, to receive funds from a customer. Each transaction is subject to a minimum transaction fee of USD 0.30.#6. Financials
This section describes the economics of the business. Aspects to be highlighted include the fixed and variable costs needed to run the business, the projected customer growth, projected number of months to breakeven, the projected number of months to cash flow, and the overall profit potential.#7. Funding
This section gives in detail the amount of funding the organization requires, how those funds will be used, and the milestones the organization hopes to achieve using the funds.Example -
PayPal is currently seeking USD 5M in Series B funding. These funds will be used to finance the development and acquisition of payment processing infrastructure in 2000Q1, the creation of marketing and training collateral to drive merchant and customer adoption in 2000Q2. At the conclusion of these activities, the company expects to in a position to begin processing transactions by 2000Q3.The 5 Paragraph Formula for an Effective Executive Summary

Paragraph 1: Provide an overview of your business
You can get your readers thinking along the track you would like them to by including a quote or statistic in the first paragraph of your executive summary.Paragraph 2: Discuss the target market and marketing strategy
Your second paragraph should comprise of a clear and concise definition of your target market, and the need or problem that your business will aim to solve.Paragraph 3: Provide an overview of operational highlights
The third paragraph should provide effective highlights like where your company offices will be located etc.Paragraph 4: Show forecasting
In the fourth paragraph, you should make sales forecast projections for one and two years since your business plan has been implemented. Calculate the break-even point, and inform the audience of what you plan next.Paragraph 5: Detail your investment needs
If your business requires any financing, this is where you should go into details about the investment needs of your business. The number you include here should be clear and should align with your projections from the previous paragraph.Conclusion
You now have the complete knowledge to draft an effective executive summary. Hopefully, this article has alleviated some of the overwhelming feelings that come while the executive summary. Remember, the executive summary is the first thing your readers read. If poorly written, it could also be the last thing they read, as they set the rest of your business plan aside unread. Now you can sync your business website with your app by using Appy Pie App Builder.Related Articles
- Reverse Brainstorming: A Powerful Backward Technique
- Jira vs. ServiceNow- A Comprehensive Guide for ITSM Solutions
- Introduction to the Forest Green Color in Graphic Designing
- Introduction to Emerald Green: Its Origins and Significance in Graphic Designing
- 10 Useful Apps for Working from Home During the COVID-19 Scare
- Top 5 Form Building Software to Accept Payments in 2023
- 50 Examples of Successful Facebook Ad Templates that Actually Work
- Best 20 Customer Service Metrics to Measure
- What is Roblox and Why is it Taking the World by Storm?
- 22 Non Profit Logo Examples for Inspiration
